Geothermal Energy: Sustainable Power from Earth’s Heat
Imagine tapping directly into the planet’s boundless warmth for clean, reliable power. In a world increasingly focused on sustainable living, geothermal energy stands out as a powerful, often overlooked, solution. It’s not just about renewable electricity; it’s about harnessing Earth’s intrinsic power to fuel a greener future.
For New Zealand, a land forged by volcanic activity and geysers, geothermal energy isn’t just a concept – it’s a fundamental part of our energy landscape and a cornerstone of our journey towards a truly sustainable lifestyle. Let’s delve into how this incredible resource works, its benefits, and its vital role in our transition away from traditional energy sources.
Table of Contents
- What is Geothermal Energy?
- How Does Geothermal Energy Work?
- The Benefits of Geothermal Energy
- Geothermal Energy in New Zealand: A Local Perspective
- Challenges and the Future of Geothermal Power
- How Consumers Can Support Sustainable Energy
- Conclusion: Tapping into Tomorrow’s Power
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- References & Sources
What is Geothermal Energy?
At its core, geothermal energy is power derived from the heat within the Earth. Deep beneath our feet, the Earth’s core generates immense heat, a remnant from the planet’s formation and from ongoing radioactive decay. This heat continuously flows outwards, warming rocks and water in the Earth’s crust.
Where this heat is concentrated near the surface, typically in volcanically active regions, we find geothermal resources. Unlike intermittent sources like solar or wind, geothermal energy provides a constant, 24/7 baseload power supply, making it a highly reliable and sustainable option.

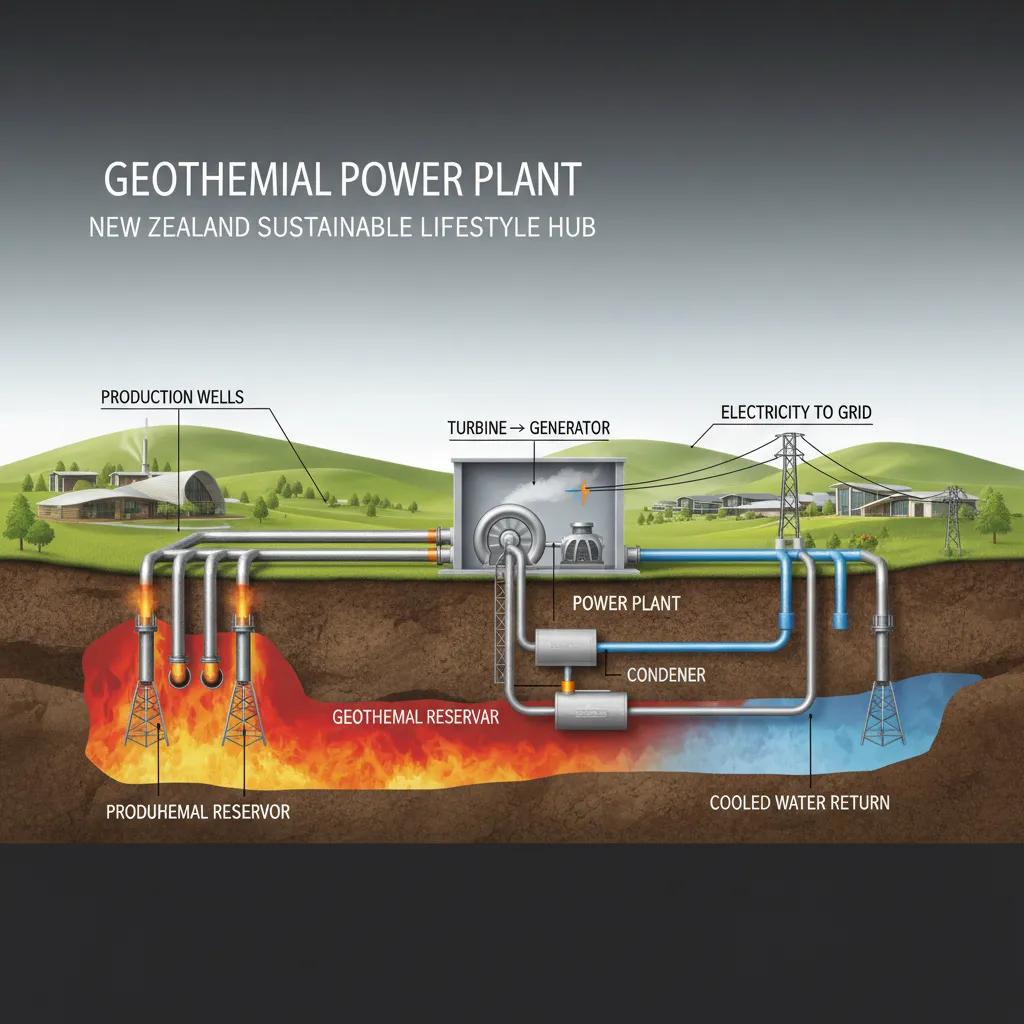
How Does Geothermal Energy Work?
Harnessing geothermal energy involves drilling wells into underground reservoirs of hot water and steam. There are several types of geothermal power plants, but the most common involve:
- Drilling Wells: Wells are drilled deep into the Earth to access reservoirs of superheated water and steam.
- Steam Production: The high-pressure, hot fluid from these wells is brought to the surface. As the pressure drops, it flashes into steam.
- Turbine Generation: This steam is then used to spin a turbine, which is connected to a generator that produces electricity.
- Reinjection: After the steam has passed through the turbine, the cooled water is injected back into the Earth to replenish the reservoir and sustain the cycle, making it a truly closed-loop, sustainable process.
“Geothermal energy represents a profound opportunity to power our lives with the very pulse of the Earth, offering a constant, clean alternative to fossil fuels.”
The Benefits of Geothermal Energy
The advantages of choosing geothermal energy: sustainable power from Earth’s heat are manifold, aligning perfectly with a sustainable lifestyle:
- Renewable and Sustainable: The Earth’s heat is virtually limitless, ensuring a continuous supply of energy for millennia.
- Low Emissions: Geothermal plants typically have a much smaller carbon footprint compared to fossil fuel plants. While some gases are released, they are significantly less potent than those from burning coal or gas.
- Reliable Baseload Power: Unlike solar or wind, geothermal operates 24/7, unaffected by weather conditions, providing a stable and predictable energy supply.
- Small Land Footprint: Geothermal power plants require relatively small land areas for their energy output, preserving natural habitats and agricultural land.
- Economic Stability: By utilising a domestic energy source, countries can reduce reliance on volatile international fossil fuel markets.
Global Impact Stat Callout:
Geothermal power plants worldwide avoid an estimated 65 million tonnes of CO2 emissions annually, equivalent to taking over 13 million cars off the road. (Source: Geothermal Energy Association)
Geothermal Energy in New Zealand: A Local Perspective
New Zealand is a global leader in geothermal energy utilisation. Our position on the Pacific Ring of Fire grants us abundant geothermal resources, particularly within the Taupō Volcanic Zone. Māori have historically used geothermal heat for cooking, bathing, and heating for centuries, demonstrating an early understanding of its value.
Today, geothermal energy is a cornerstone of New Zealand’s electricity generation. It plays a critical role in our national goal of achieving 100% renewable electricity by 2030 (in a normal hydrological year). Major geothermal fields like Wairākei and Kawerau exemplify our commitment to this clean energy source.
New Zealand’s Geothermal Contribution:
Geothermal energy consistently contributes over 17% of New Zealand’s total electricity generation, making it our third-largest source of renewable power. (Source: MBIE Energy in New Zealand)

Challenges and the Future of Geothermal Power
While the benefits are substantial, geothermal energy development isn’t without its challenges:
- High Upfront Costs: Drilling and plant construction are expensive, requiring significant initial investment.
- Geological Specificity: Usable geothermal reservoirs are geographically constrained, limiting widespread deployment.
- Environmental Considerations: While generally clean, some projects can release minor amounts of greenhouse gases (CO2, H2S) or cause seismic activity, though these are typically well-managed.
- Resource Management: Careful management of geothermal reservoirs is essential to ensure their long-term sustainability.
Despite these hurdles, the future of geothermal energy: sustainable power from Earth’s heat is bright. Advancements in Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) are making it possible to access geothermal resources in more locations, potentially unlocking vast new energy reserves. As technology improves and costs decrease, geothermal will undoubtedly play an even larger role in our global energy transition.
How Consumers Can Support Sustainable Energy
As individuals living in New Zealand and beyond, we can contribute to the growth of sustainable energy, including geothermal:
- Choose Green Energy Plans: If your electricity provider offers options to source power from renewables, opt for them.
- Reduce Your Consumption: The most sustainable energy is the energy you don’t use. Improve home insulation, use energy-efficient appliances, and turn off lights.
- Advocate for Policy: Support local and national policies that promote renewable energy development and sustainable practices.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Understand where your energy comes from and share that knowledge.

Conclusion: Tapping into Tomorrow’s Power
Geothermal energy offers a compelling vision for a sustainable future, literally drawing power from the Earth beneath our feet. Its reliability, low emissions, and constant output make it an indispensable component of New Zealand’s renewable energy mix and a vital player in the global fight against climate change.
As we continue our journey towards a more sustainable lifestyle, understanding and supporting sources like geothermal energy: sustainable power from Earth’s heat is crucial. By embracing the power of our planet, we can secure a cleaner, more stable energy future for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is geothermal energy truly renewable?
Yes, geothermal energy is considered a renewable energy source. The heat within the Earth is continuously replenished, and modern geothermal plants reinject cooled water back into the reservoir to maintain pressure and resource longevity, ensuring its sustainability over very long periods.
What are the main environmental impacts of geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy has a significantly lower environmental impact than fossil fuels. Potential impacts include minor greenhouse gas emissions (though much less than coal or gas), land use for power plants, and in rare cases, induced seismicity. However, these are generally well-managed and mitigated compared to other energy sources.
Why isn’t geothermal energy more widespread globally?
The primary reasons are geographical constraints (suitable geothermal reservoirs are not universally distributed) and high upfront drilling and construction costs. However, technological advancements like Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) are expanding its potential reach.
How does New Zealand benefit from geothermal energy?
New Zealand benefits immensely from geothermal energy by having a reliable, baseload, and domestically sourced renewable power supply. This reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels, contributes significantly to our climate goals, and supports local economies in regions like the Taupō Volcanic Zone.
References & Sources
- Geothermal Energy Association. (n.d.). Geothermal Basics. Retrieved from https://www.geo-energy.org/our-impact/geothermal-basics
- Ministry of Business, Innovation & Employment (MBIE). (2023). Energy in New Zealand. Retrieved from https://www.mbie.govt.nz/building-and-energy/energy-and-natural-resources/energy-data-and-modelling/energy-publications/energy-in-new-zealand/
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). (2020). Geothermal Power: Technology Brief. Retrieved from https://www.irena.org/solar/Geothermal
- New Zealand Geothermal Association (NZGA). (n.d.). About Geothermal. Retrieved from https://nzgeothermal.org.nz/about-geothermal/
