Solar Battery Storage: Maximizing Self-Sufficiency in NZ
Unlock true energy independence and resilience for your New Zealand home with advanced solar battery solutions.

In an era where energy independence and sustainable living are more critical than ever, solar battery storage NZ is emerging as a cornerstone for Kiwi homeowners. Far beyond simply generating clean power, adding battery storage transforms your solar PV system into a robust, self-sufficient energy hub. It’s about taking control of your electricity, enhancing your home’s resilience, and significantly reducing your reliance on the grid.
Whether you’re looking to minimise your carbon footprint, future-proof against rising electricity costs, or ensure reliable power during outages, understanding solar battery storage is your next vital step. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to make an informed decision for your New Zealand property.
1. Benefits of Solar Battery Storage
Investing in solar battery storage for your New Zealand home offers a multitude of advantages, transforming how you interact with and consume energy. It’s not just about storing power; it’s about empowering your household.
- Energy Independence & Self-Sufficiency: Store excess solar energy generated during the day and use it at night, dramatically reducing your reliance on grid electricity. This means fewer power bills and greater peace of mind.
- Reduced Electricity Bills: By consuming your own stored solar power during peak tariff hours, you minimise expensive grid imports. This can lead to substantial long-term savings, especially with NZ’s varying time-of-use rates.
- Blackout Protection & Resilience: A properly configured battery system provides backup power during grid outages, keeping essential appliances running. This is invaluable in New Zealand, where weather events can sometimes disrupt power supply.
- Environmental Impact: Maximising your self-consumption of solar energy further reduces your carbon footprint, contributing directly to New Zealand’s sustainability goals.
- Grid Stability & Demand Management: With smart battery systems, you can actively participate in demand response programmes, potentially earning credits for supporting the grid during peak times.
2. Types of Solar Batteries & Capacity
When considering solar battery storage NZ, understanding the different types and their respective capacities is crucial for making the right choice for your needs and budget. Each technology comes with its own set of characteristics.
Common Battery Technologies
The market is primarily dominated by a few key technologies, each offering distinct advantages:
- Lithium-ion Batteries (LiFePO4, NMC): These are the most popular choice for modern solar storage due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and excellent efficiency. Lithium Ferro Phosphate (LiFePO4 or LFP) variants are particularly favoured for their safety and durability.
- Lead-Acid Batteries (AGM, Gel, Flooded): A more traditional and cost-effective option, though with a shorter lifespan, lower efficiency, and higher maintenance requirements than lithium-ion. They are often used in off-grid or remote setups where initial cost is a primary concern.
- Flow Batteries: While less common for residential use currently, flow batteries offer very long lifespans, excellent safety, and are fully recyclable. They store energy in liquid electrolytes contained in external tanks, allowing for easy scalability.
Understanding Battery Capacity
Battery capacity is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and indicates how much energy the battery can store. Your ideal capacity will depend on:
- Your daily energy consumption (especially during non-solar hours).
- The amount of solar energy your system generates.
- Your desired level of self-sufficiency or backup duration.
Most residential solar battery storage NZ systems range from 5 kWh to 20 kWh, often expandable with modular units.
| Feature | Lithium-ion (e.g., LiFePO4) | Lead-Acid (e.g., AGM) |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan (Cycles) | 4,000 – 10,000+ | 500 – 2,000 |
| Depth of Discharge (DoD) | 90% – 100% | 50% |
| Efficiency (Roundtrip) | 90% – 98% | 70% – 85% |
| Maintenance | Very Low / None | Moderate (ventilation, topping up for flooded) |
| Cost (per kWh) | Higher upfront, lower long-term | Lower upfront, higher long-term |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, higher resource intensity | Recyclable (but less efficient) |

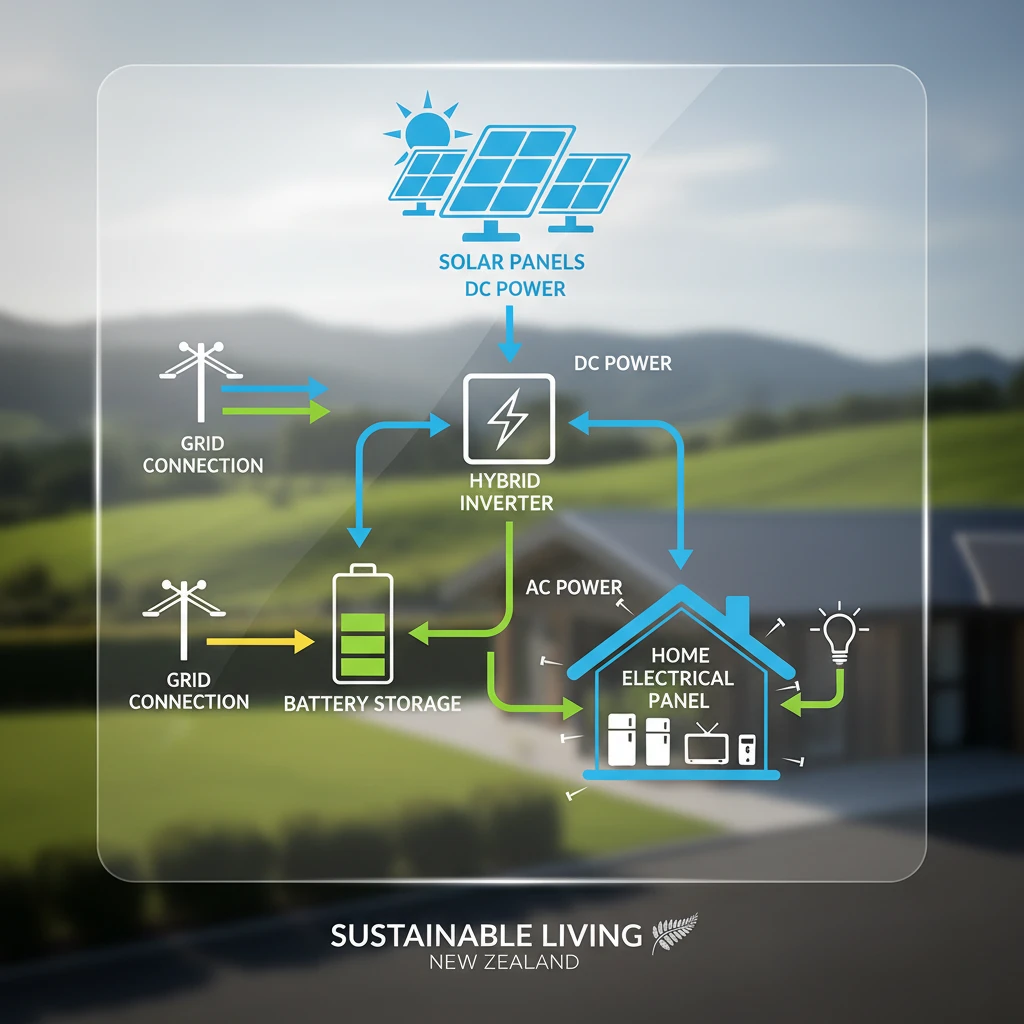
3. Integrating Batteries with Your Solar System
Seamless integration is key to maximising the performance of your solar battery storage NZ system. This involves understanding how batteries connect to your existing or new solar setup and what components are required.
AC-Coupled vs. DC-Coupled Systems
- DC-Coupled: In this setup, the solar panels and battery share the same inverter. This is often the most efficient option for new installations, as solar power can flow directly from panels to the battery without multiple conversions.
- AC-Coupled: This involves separate inverters for the solar panels and the battery. It’s an excellent choice for retrofitting batteries to an existing grid-tied solar system, as it allows for independent operation and easy expansion.
Key Components for Integration
- Hybrid Inverter: Crucial for most modern setups, a hybrid inverter manages both solar generation and battery charging/discharging, facilitating seamless power flow.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Integrated within the battery, the BMS monitors and protects the battery cells, optimising performance and extending lifespan.
- Energy Metering: Smart meters are essential for monitoring energy production, consumption, and battery status, providing valuable insights for optimisation.
- Switchgear & Safety: Proper electrical wiring, circuit breakers, and isolation switches are vital for safety and compliance with New Zealand electrical standards.
“Choosing the right integration method depends heavily on your current solar setup and future energy goals. Consulting with a certified solar installer in NZ is paramount to ensure optimal performance and compliance.”
4. Optimizing Energy Use with Storage
Having solar battery storage NZ is just one part of the equation; effectively managing and optimising its use unlocks its full potential. Smart energy management systems allow you to get the most out of your stored power.
Strategies for Maximising Battery Value
- Time-of-Use (TOU) Optimisation: Charge your battery during off-peak hours (if grid-connected and tariffs allow) or purely from solar during the day, then discharge it during expensive peak periods. This significantly reduces your electricity costs.
- Load Shifting: Schedule energy-intensive appliances (like washing machines or dishwashers) to run during the day when solar power is abundant, or during off-peak hours using stored battery power.
- Weather Forecasting Integration: Advanced systems can integrate with weather forecasts, adjusting charging and discharging cycles to account for cloudy days or anticipated high demand, ensuring you always have sufficient power.
- Excess Energy Management: Decide whether to export excess stored energy back to the grid for credits (if available with your retailer) or save it for future consumption, based on economic benefits and self-sufficiency goals.
Many modern battery systems come with integrated apps and online portals, giving you real-time insights into your energy production, consumption, and battery status. This data empowers you to make smarter decisions about your energy use.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Solar Battery Storage NZ
How much does solar battery storage cost in NZ?
The cost of solar battery storage NZ varies widely based on capacity, brand, and installation complexity. A typical residential lithium-ion system can range from NZD $8,000 to $20,000, excluding solar panels and inverter costs. While a significant upfront investment, long-term savings on electricity bills and increased energy independence offer substantial value.
How long do solar batteries last in New Zealand?
Most modern lithium-ion solar batteries come with warranties of 10-15 years or a guaranteed number of cycles (e.g., 4,000-6,000 cycles). With proper use and maintenance, you can expect them to perform effectively for well over a decade, with some designs lasting even longer.
Can I go completely off-grid with solar and battery storage in NZ?
Yes, it is possible to go completely off-grid in NZ with a sufficiently sized solar array and battery bank. However, this typically requires a larger investment in both solar panels and battery capacity, often with a backup generator for prolonged periods of low solar generation. Most urban and suburban homeowners opt for a grid-tied system with battery backup for enhanced resilience rather than full off-grid living.
What size solar battery do I need?
The ideal battery size depends on your daily electricity consumption, particularly during hours when your solar panels aren’t generating (e.g., night-time), and your desired backup duration. A professional installer will conduct an energy audit of your home to recommend the optimal battery capacity for your specific needs.
Are there any grants or subsidies for solar battery storage in NZ?
While there are no broad national grants specifically for solar battery storage in New Zealand currently, some regional councils or community trusts may offer local initiatives or financing options. It’s advisable to check with your local council and energy efficiency organisations like EECA for any current programmes.
References/Sources
- Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority (EECA) – www.eeca.govt.nz
- Vector Energy Data – www.vector.co.nz/personal/electricity/network-data
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) Publications – www.irena.org
- Sustainable Energy Association New Zealand (SEANZ) – www.seanz.org.nz
- Ministry of Business, Innovation & Employment (MBIE) – www.mbie.govt.nz